High Performing Thermoelectric 2D Sb₂Te₃ and Bi₂Te₃ Nanoplates
High Performing Thermoelectric 2D Sb₂Te₃ and Bi₂Te₃ Nanoplates
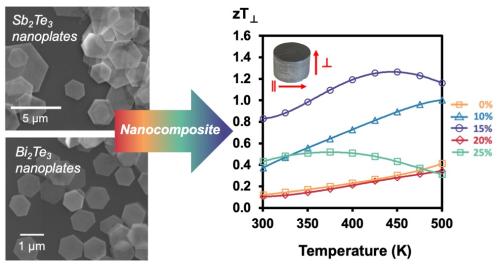
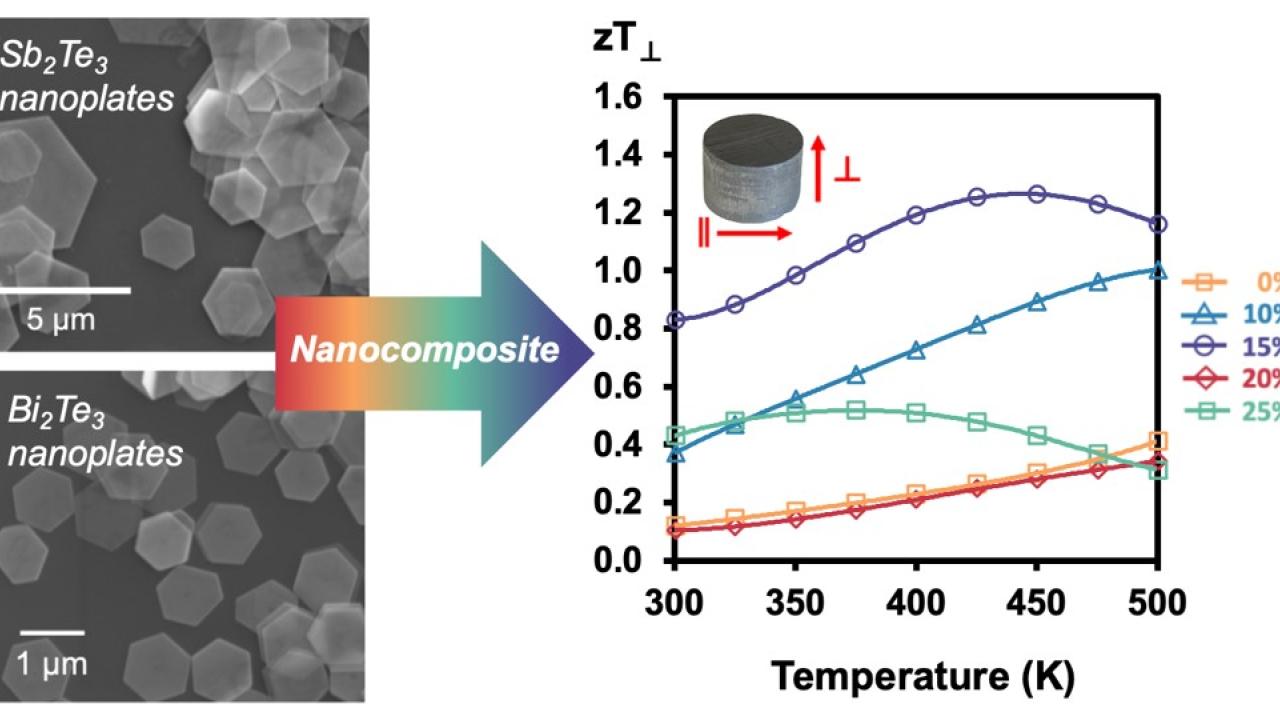
In a recent publication (Kimberly and coworkers, ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2023) the Kauzlarich Lab reports on the synthesis of two-dimensional (2D) nanoplates of the layered chalcogenides, Sb₂Te₃ and Bi₂Te₃, and investigation of the thermoelectric properties of their composites. The two materials, Sb₂Te₃ and Bi₂Te₃, were synthesized as hexagonal nanoplates via a solution route. Characterization via electron and atomic force microscopies reveal that the as-synthesized Sb₂Te₃ and Bi₂Te₃ vary drastically from one another in their lateral and vertical dimensions. Thermoelectric properties in the parallel and perpendicular directions were measured, revealing strong anisotropy with a significant reduction to thermal conductivity in the perpendicular direction. The Seebeck coefficient is also increased dramatically in the nanocomposites which is an effect that is attributed to energy carrier filtering at the nanoplate interfaces. Overall, these enhanced thermoelectric properties lead to a drastic increase in the thermoelectric performance in the perpendicular direction, with zT ∼ 1.26, which is one of the highest for this system.
More information at:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsaelm.3c00385?ref=pdf